Artificial Intelligence (AI), as pictured in sci-fi movies, is now becoming a reality. Its ability to change work dynamics across various industries and, furthermore, to change our lives has become increasingly evident.
There are some risks associated with AI that might prove more dangerous to humanity than beneficial. Some of the risks associated with its deployment are bias, discrimination, and lack of transparency. To mitigate these risks, UNESCO formed an agreement on the ethics of AI, whereas the US has passed certain laws and is working on further regulations. However, right at the forefront of this charge is the European Union (EU), which took the lead in creating comprehensive frameworks and laws to regulate AI.
Jump to section
EU AI Regulations 2018
The EU AI regulations have been discussed in the EU since 2018 with the publication of the European Commission’s “Communication on Artificial Intelligence for Europe.” The EU’s AI strategy emphasized the importance of ethical, legal, and socio-economic guidelines for AI development.
Specifically, the vision is to have an AI that respects fundamental human rights, values, and ethical principles while emphasizing the need for trustworthy AI. As part of the communication, the EU was also urged to coordinate AI regulations in the union, as well as cooperate with foreign cooperation on AI governance.
While not specifically targeting AI, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) played a crucial role in shaping the EU’s approach to AI regulations. Implemented in May 2018, the GDPR focused on protecting individuals’ data rights, including personal data used in AI systems. GDPR influenced subsequent AI regulations, particularly those concerning data privacy, transparency, and accountability.
EU AI Regulations 2019
In April 2019, the EU’s High-Level Expert Group on AI (AI HLEG), established by the European Commission, published “Ethics Guidelines for Trustworthy AI.” which set out seven key principles for AI development and deployment. These principles are –
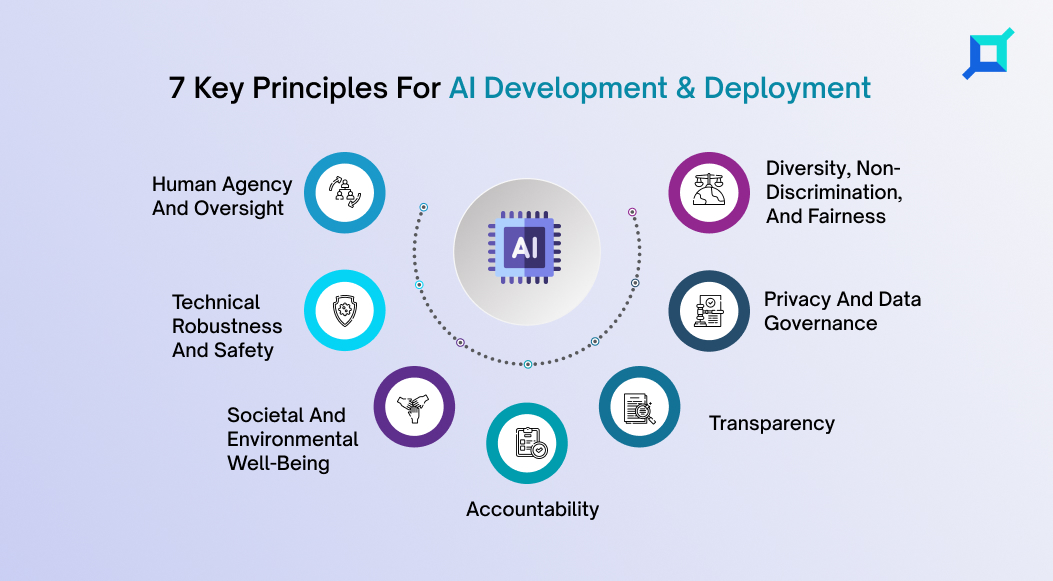
As part of these, a framework was established for AI assessments that involved evaluating the impact of artificial intelligence on fundamental rights, such as privacy, non-discrimination, and freedom of expression. This also served as a valuable reference for subsequent regulatory efforts.
EU AI Regulations 2020
In February 2020, the EU published a “White Paper on AI: A European Approach to Excellence and Trust” to plan future AI regulations. The white paper proposed a risk-based approach to AI regulation, which classified AI systems according to their level of risk and required different levels of oversight and transparency depending on their risk level.
It also proposed a range of measures to promote innovation and investment in AI, such as increased funding for research and development and creating a European AI marketplace.
EU AI Regulations 2021 – 2023
Building upon earlier initiatives, the European Commission introduced a landmark proposal, the “Regulation on a European Approach for Artificial Intelligence” (AI Act), in April 2021. The AI Act aims to establish a harmonized legal framework for AI systems, balancing innovation and protection.
The regulation requires AI systems to be designed and developed in a way that respects fundamental rights and freedoms, such as the right to privacy and the right to non-discrimination. It introduces several notable provisions –
- The AI Act prohibits AI systems that manipulate human behavior in a deceptive or harmful manner, such as social scoring for government surveillance.
- The AI Act mandates transparency regarding AI’s purpose, nature, and consequences for users. It requires high-risk AI systems to undergo conformity assessments by authorized bodies, ensuring compliance with strict data and technical requirements.
- The AI Act imposes obligations for developers and providers of AI systems, including comprehensive documentation, robust data governance, and human oversight.
The AI Act sparked intense discussions among stakeholders, including AI developers, businesses, civil society organizations, and policymakers.
Feedback was considered to refine and amend the proposal, addressing concerns such as the scope of high-risk AI applications, the potential impact on innovation, and the balance between regulation and competitiveness.
The European Parliament and the Council actively reviewed the AI Act, ensuring it aligns with the diverse perspectives and requirements of EU member states. The draft of which was passed by the EU lawmakers on April 27, 2023, and was further approved by a committee of lawmakers in the EU parliament on May 12, 2023, taking it a step closer to becoming the law.
In addition to the AI Act, the EU is exploring complementary regulations to address data sharing for AI development while safeguarding the privacy and data protection via the Data Governance Act (DGA). It was proposed in November 2020 with the aim of facilitating data sharing across sectors and EU countries while ensuring data protection and fostering trust.
It is a set of rules designed to expand access to public sector data for developing new products & services. The DGA applies not only to personal data but to any digital representation of acts, facts, or information.
The rules came into force on June 23, 2022, and will take effect in September 2023. It creates a framework to facilitate data sharing and provides a secure environment for organizations or individuals to access information.
Conclusion
The EU’s journey towards AI regulation showcases its commitment to ensuring ethical, transparent, and accountable development and deployment of AI systems.
From the inception of guidelines to the proposed AI Act, the EU has taken significant strides to balance fostering innovation and safeguarding fundamental rights. While the AI Act is about to become law, it represents a milestone in shaping the future of EU AI regulations.
These efforts position the EU as a leading authority in the global AI landscape, emphasizing the importance of responsible AI development and deployment for the benefit of society. Moreover, if you need any more information on EU AI regulations, innovative AI solutions, etc, feel free to get in touch with us…