Over the past few decades, Artificial Intelligence has increasingly become an important and influential technology in various aspects of our lives. AI has left its mark in various areas of education, finance, the environment, agriculture, entertainment, and healthcare.
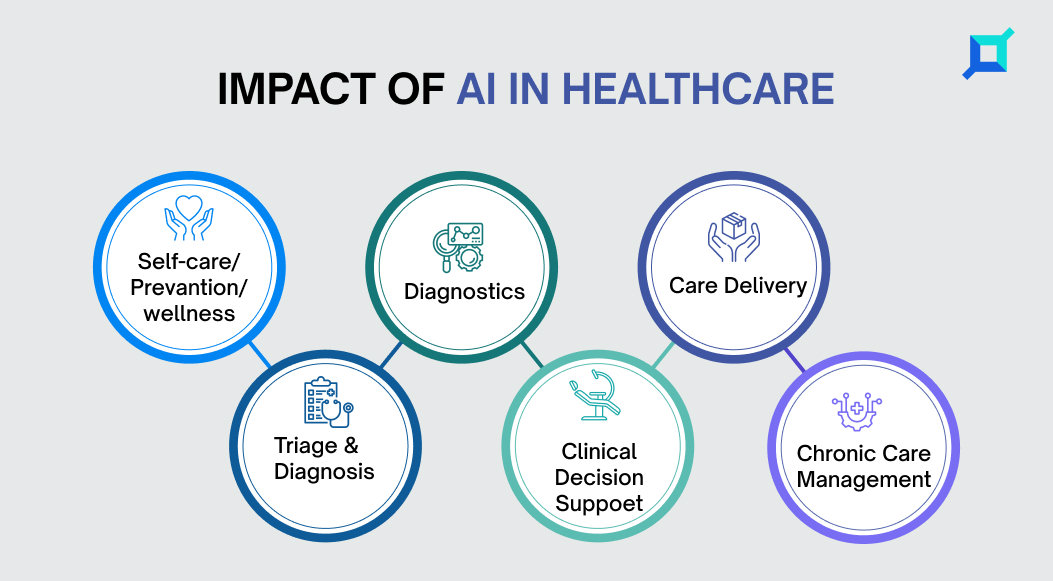
Recently, healthcare has been considered one of the primary areas where AI is making a big impact, particularly in disease diagnosis and treatment management. AI has emerged as a crucial technology in the healthcare industry, with a growing presence in various aspects of patient care. It’s transforming healthcare by improving the accuracy of diagnoses, enhancing the speed and efficiency of treatments, and increasing patient safety.
Jump to section
Categorization Of Data In AI
Making any AI technology work efficiently requires a large amount of data on which it can be trained. This data in AI is categorized as structured and unstructured data. Structured data refers to data organized in a specific format, such as electronic health records, laboratory results, and billing codes. Unstructured data is not organized in a specific format, such as medical images or physician’s notes.
Training machine learning models on structured and unstructured data requires different techniques. Structured data can be easily processed using traditional machine-learning algorithms like decision trees and random forests. These algorithms are designed to handle data in structured formats and can easily identify patterns and trends in large datasets.
Unstructured data, however, requires more advanced machine learning techniques, such as deep learning algorithms. Deep learning algorithms use neural networks to learn from unstructured data, such as medical images, and identify patterns and features indicative of a disease or condition. These algorithms are trained using large datasets of labeled medical images, where each image is tagged with the corresponding disease or condition.
Training machine learning models on healthcare data, whether structured or unstructured, requires a large and diverse dataset. The more data the machine learning algorithm has access to, the more accurate it can become in identifying patterns and predicting outcomes.
Additionally, data quality is important, as errors or inconsistencies in the data can result in inaccurate predictions.
AI Datasets Usage In Healthcare
AI relies heavily on datasets to train machine learning algorithms and improve the accuracy of diagnostic and treatment outcomes. Some of the datasets that are commonly used in Artificial Intelligence in healthcare are –
Electronic Health Records (EHR)
EHRs contain patient medical histories, diagnosis codes, and treatment information. Machine learning algorithms can analyze EHRs to identify patterns and trends indicating a disease or condition. Moreover, EHRs can also identify patients at high risk of developing certain diseases or conditions.
Medical Imaging Datasets
It contains images such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. These datasets train machine learning algorithms to detect patterns and identify anomalies in medical images. By analyzing these images, AI can identify early signs of diseases and improve the accuracy of diagnosis.
Genomic Datasets
These datasets contain genetic information that can be used to predict a patient’s risk of developing certain diseases. AI can analyze genomic data to identify genetic mutations that may be linked to diseases such as cancer or Alzheimer’s disease.
Wearables And IoT Data
It can track a patient’s vital signs, like blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen levels. This data can be used to monitor patients remotely and identify early signs of a medical condition. In addition, Machine Learning algorithms can analyze this data to predict potential health issues and improve patient outcomes.
Clinical Trial Data
This sort of data contains information about the safety & efficacy of drugs and medical devices. Machine learning algorithms can analyze this data to identify potential side effects or drug interactions and improve treatment outcomes.
AI can potentially improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs by analyzing these datasets.
Applications Of Artificial Intelligence (AI) In Healthcare
AI in healthcare can be used in predicting early stroke detection to seasonal flu, suggesting medical treatments, to being a virtual assistant. Some Artificial Intelligence in healthcare examples is becoming popular; details below –
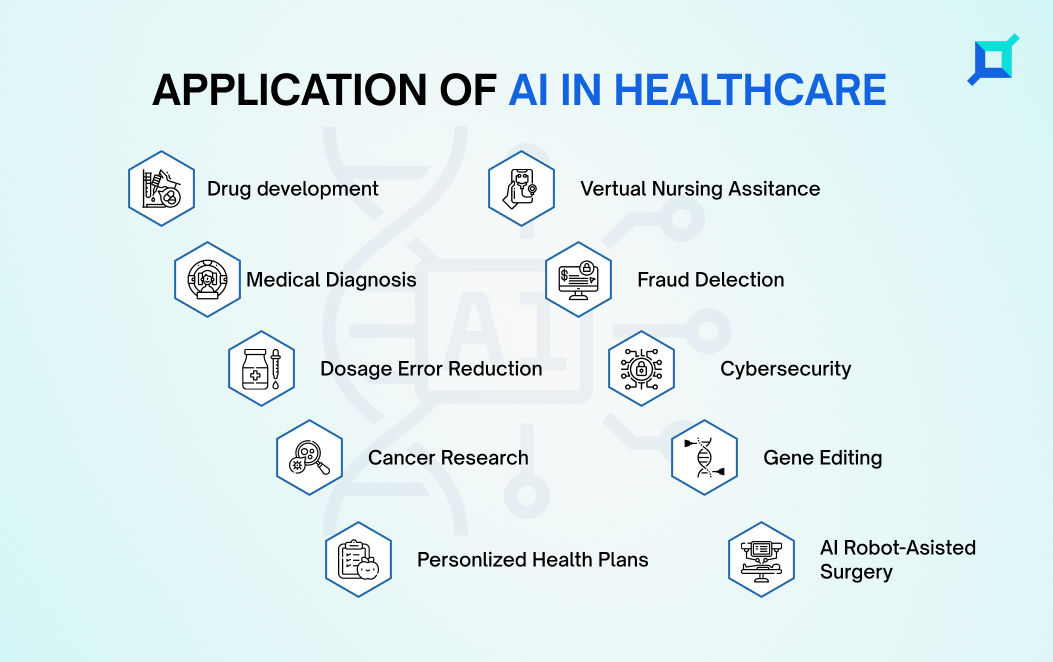
1. Medical Imaging Analysis
Artificial Intelligence helps clinicians analyze medical images more accurately and efficiently. ML algorithms are trained on enormous datasets of medical images, enabling them to detect patterns and identify anomalies in the images.
AI-powered medical imaging systems can help identify diseases early, enabling clinicians to provide timely interventions and improve patient outcomes.
For example, AI-powered systems analyze X-rays and CT scans to detect lung cancer and other diseases.
2. Disease Diagnosis And Treatment
AI is used to help clinicians diagnose diseases and develop treatment plans. Machine learning algorithms can analyze patient data, such as medical records and lab results, and provide clinicians with personalized treatment recommendations.
As an example, IBM’s Watson Health has been used to devise personalized treatment plans for cancer patients, thereby reducing diagnosis and treatment times.
3. Electronic Health Records (EHR)
AI is being employed to analyze EHR to identify patterns and trends that can help improve patient care. ML algorithms can analyze large datasets of EHR to identify patients at high risk of developing certain diseases or conditions.
For example, AI can analyze a patient’s medical history to identify those at high risk of developing heart disease and provide personalized treatment recommendations.
4. Virtual Nursing Assistants
AI-powered virtual nursing assistants can help patients manage their health and well-being. Virtual nursing assistants can guide patients on medication, exercise, and diet and alert healthcare providers if a patient’s condition changes or they need immediate medical attention.
5. Predictive Analytics For Hospital Operations
Artificial Intelligence predicts patient demand for emergency services, enabling hospitals to allocate resources more efficiently and reduce patient wait times. Additionally, predictive analytics can also predict patient outcomes based on their medical history, allowing healthcare providers to identify patients at high risk of developing complications and provide timely interventions.
What Challenges Usually Occur When Employing AI In the Healthcare Sector?
AI for healthcare has tremendous potential to transform the industry, but several challenges must be addressed before it can be adopted at a large scale. Some of the major challenges to adopting AI in healthcare are –
1. Data Privacy & Security
Healthcare data is sensitive and confidential, and patient privacy must always be protected. Adopting Artificial Intelligence for healthcare requires storing and processing large amounts of patient data, which can boost the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks.
Ensuring data privacy and security is a major challenge for healthcare organizations looking to implement AI solutions.
2. Integration With Existing Systems
Most healthcare organizations have complex IT systems, and integrating AI solutions into these systems can be challenging.
AI systems must be able to communicate with existing EHR systems and other clinical systems, which can require significant resources and time.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare is a heavily regulated industry, and AI solutions must comply with numerous regulations, such as HIPAA and GDPR.
Ensuring regulatory compliance can be a significant challenge for healthcare organizations looking to implement AI solutions.
4. Limited Data Availability
While an abundance of healthcare data is available, much of it is not easily accessible or usable for AI applications.
Data fragmentation, limited interoperability between systems, and data quality issues can make gathering the necessary data for AI solutions difficult.
5. Lack of Trust & Acceptance
There is still a lack of trust and acceptance among healthcare providers and patients regarding AI in healthcare.
Many healthcare providers hesitate to adopt AI solutions due to concerns about job displacement, liability, and loss of control over patient care. Patients may also hesitate to trust AI with their healthcare due to privacy and data security concerns.
Wrapping Up
Artificial Intelligence has revolutionized healthcare by enhancing diagnostics, enhancing patient outcomes, and reducing the burden on healthcare professionals. The use of AI in healthcare has enabled the development of predictive models that can identify potential health issues and recommend preventative measures.
Moreover, AI-based systems accurately detect diseases like cancer and heart disease. With the continued development of AI technology, it is expected that the role of AI in healthcare will continue to grow, bringing about further improvements in patient care and outcomes.
However, it is crucial to note that the use of AI in healthcare also raises concerns about privacy, data security, and ethics, which need to be carefully considered and addressed. So, if you are thinking of using AI in your business, connect with Infrablok and get dedicated AI/ML experts who can help you fulfill your needs in no time.